Flexing a Different “Conversational” Muscle
This is an article Glenna and I wrote for The Systems Thinker. It is republished here in its entirety.
Today, many management theorists and practitioners argue that organizations are attempting to move from one paradigm, or worldview, to another (see “How Dialogue Supports Our Expanding Worldview”). Specifically, we’re shifting from the Newtonian approach (the inner circle in the diagram) – which served us so well during the Industrial Revolution – to what’s known as a quantum approach (the outer circle). The Newtonian perspective emphasizes linear thinking, top-down decision-making, and competition. The quantum perspective stresses systems thinking, shared leadership, collaboration, and other approaches that are far more appropriate in today’s rapidly accelerating information and knowledge-based economy.
The inner circle describes Newtonian approaches to managing and organizing. The outer circle describes quantum approaches. Both are valuable, but the need for quantum approaches is growing as organizational life becomes more complex.
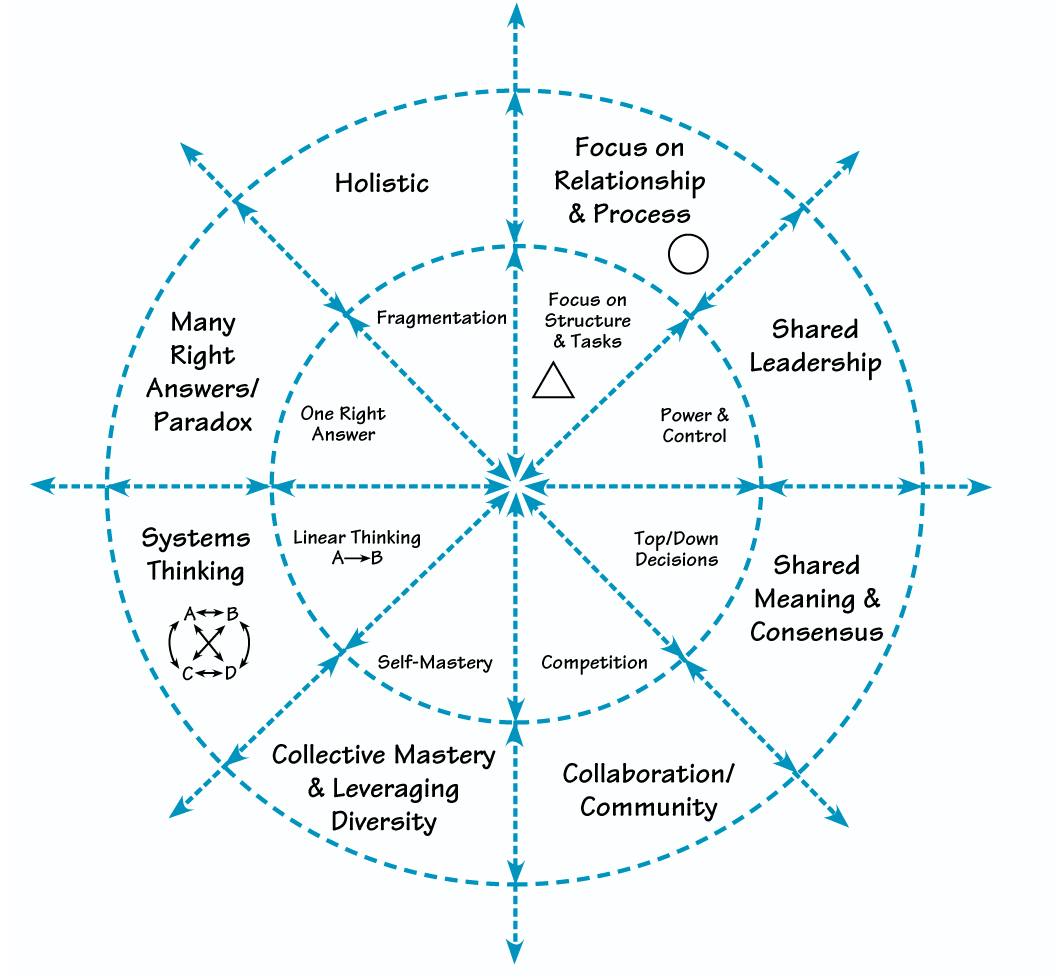
Neither worldview is right or wrong; however, each offers unique advantages under specific circumstances. Indeed, in the diagram, the dotted lines that separate the two paradigms imply permeable, flexible boundaries. Moreover, the arrows suggest that other ways of organizing will also evolve.
But for now, we seem to be lodged in the Newtonian mode of operating, with our eyes cast toward the quantum one. Most of us say we want to have shared leadership and more collaboration in our organizations. We want to foster systems thinking and to leverage diversity. But the inertia of older ways of working often keeps us from moving in these directions.
Dialogue can play a key role in an organization’s ability to adopt a quantum approach to day-to-day operations and challenges, because it focuses on how diverse perspectives and interests within a system relate to one another. What exactly is dialogue? In its simplest sense, dialogue is a form of conversation intended to build shared understanding and learning around how the members of a group think about a given issue or question. Dialogue is markedly different from discussion, or debate. We dialogue in order to learn from each other and clarify what we are trying to accomplish together.
The core skills and practices of dialogue are suspension of judgment, listening, reflection, assumption identification, and inquiry.
Suspension of Judgment. In conversation, it is our nature to make value judgments quickly: We often make assessments that what someone said is good or bad, right or wrong, etc. Suspension of judgment isn’t about stopping judging – we couldn’t do that if we tried. Rather, it’s about noticing what our judgments are – and then holding them lightly so that we can still hear what others are saying, even when it may contradict our own judgments.
Listening. In Westernized, modern cultures, people normally listen to others from the standpoint of their own personal interests. To listen in dialogue is to flex a very different conversational “muscle.” Not only must we listen for our own and others’ voices, we must also attend to the larger picture of what everyone is voicing together.
Reflection. Reflection is the capacity to wait in silence, to consciously slow the rate of speed with which the conversation might take place, and to see beyond our immediate responses to what we are hearing, thinking, and feeling in the moment.
Assumption Identification. Our assumptions and beliefs about how the world works powerfully shape the decisions and results we get in organizations. Yet we often gloss over our assumptions, never challenging ourselves to see what drives our decisions at a deeper level. Our ability to think creatively has a lot to do with our ability to surface and examine our underlying assumptions.
Inquiry. Another core capacity of dialogue is inquiry; that is, the art of asking questions to clarify thinking and generate new possibilities. Inquiry requires a keen sense of curiosity about learning what others might say about a topic of conversation. It also requires the ability to formulate open-ended questions that draw out others’ opinions.
Transforming Organizational Culture
Just as dialogue can dramatically impact our worldview, once awareness of the power and capacities of dialogue arises in an organization, the entire culture may ultimately be transformed. Dialogue stimulates deep change, not only in the pace and approach with which people make decisions but also in their attitudes toward diversity, questions, and other important concepts.
Becoming Self-Directed. One of the most noticeable attitude shifts that dialogue can catalyze is the movement from being “other-directed” to being “self-directed.” What do these phrases mean? Being other-directed indicates waiting for some outside authority to give direction, while being self-directed stems from the capacity to listen within one’s self for what is appropriate in a given context. Dialogue helps us build a system-wide view of what is happening, because it lets us see the many connections between actions and functions in a team and throughout the whole organization. Once we have the big picture before us, we can more easily see our place in it. As a result, we often begin taking more responsibility for our own day-to-day decisions after engaging in dialogue. Over time, we become less dependent on managers or supervisors for answers and direction. Decision-making diffuses throughout the organization, and individuals are able to align their behaviors with the organization’s core vision because they can see it in its entirety.
Dialogue helps us build a system-wide view of what is happening, because it lets us see the many connections between actions and functions in a team and throughout the whole organization
Valuing Diversity. Another core shift happens in attitudes toward diversity – whether it’s diversity of gender, race, ideas, culture, sexual orientation, or all of these. While many tout the idea of diversity as valuable in organizations today, in reality, diversity often makes us uncomfortable. We unconsciously desire to be with people like us and seldom go out of our way to seek out diverse opinions. Indeed, many people view diversity of any sort as a source of conflict and an obstacle to decision-making.
But something problematic happens when we cluster only with like-minded people: We have trouble generating new ideas and innovations. We also lose sight of the larger picture that the expression of diverse perspectives can create. And without that larger picture, our decisions stem from a narrow perspective. Simply put, without inviting and exploring diverse viewpoints, we risk making unwise, ineffective, and downright dangerous decisions.
Fortunately, dialogue provides the tools for navigating these differences. As people feel more confident using the tools, diversity and conflict become less frightening. Instead, they become sources of creativity and new energy.
Staying in a Place of Inquiry. Another shift in attitude that occurs as people practice dialogue is that individuals gain a new appreciation and tolerance for questions. In Western cultures, we often feel compelled to drive for answers. We don’t like to leave questions unanswered and problems unsolved. If a question pops up, we want a fast answer. In dialogue, we seek to stay with questions long enough to allow diverse perspectives to contribute to the generation of more possibilities – thus promoting new learning and creativity.
Attending to the Larger Picture. As a related shift, dialogue teaches us to attend to the larger picture, which ties back to the sense of shared responsibility we explored above. When we practice dialogue, we place more value on seeing the whole, seeing how the parts all add up to more than their simple sum. Newtonian thinking takes a particularly narrow focus on things by breaking problems and challenges down into small, analytical, bite-size pieces. Because dialogue is integrative, it teaches us to pay more attention to the whole: “Where is the whole company going? What are we doing together? How does my part contribute to the whole?”
Practicing Dialogue
To reap the benefits of dialogue, you don’t have to practice it only in a formal sense. Once you understand dialogue’s core capacities and begin practicing them, you can weave them into any conversation. People often get confused about this. They think that to dialogue, everyone has to sit in a circle, with serious expressions, and practice in a structured way every week. While this is the most complete form of dialogue, it isn’t the only way to hone these capacities.
What are the best avenues for introducing this form of conversation, and the skills that support it, that will deliver the most value to your organization? Below are some easy-to-implement suggestions.
Leading Change by Example People often ask, “Well, what if I’m talking with people who don’t know dialogue?” Our advice is: Try practicing it anyway – your modeling just might rub off on them! Many of the principles behind dialogue are actually quite intuitive; it’s just that when we are conversing with others in a competitive environment, we tend not to use them. By trying to remain consciously aware of these capacities, we will be more likely to use them. This kind of skills modeling is your most powerful way of influencing others to give dialogue a try.
This may sound simple, but of course it can be hard to change our conversational styles – particularly in a culture that emphasizes win-lose metaphors of war and sports and that equates quick results with success and even survival. Yet such change is possible – through small shifts made one person, and one moment, at a time.
Experimenting with Personal Practice. One great way to both model dialogue skills and start introducing dialogue at work is to begin a personal practice of the skills. Here’s how you might do this: Choose a skill area, such as suspension of judgment. Outline a plan for working with the skill. For example: “I will notice my judgments and consciously suspend them in designated conversations. I will notice how my judgments affect my listening. I will notice what impact suspending my judgments has on my listening and on the overall quality of my conversations.” At the close of each day, review your daily practice and note any specific observations and learning (see “Tips for Practicing Dialogue Skills”).
TIPS FOR PRACTICING DIALOGUE SKILLS
Suspension of Judgment
- Notice your judgments and the impact they have on your listening in at least one conversation each day
- Try using your imagination to suspend your judgments and continue to listen. Each time a judgment arises, suspend it, and continue to listen. Notice what happens as a result
- Sit quietly for five minutes. Simply focus on your breathing. Notice each time you are distracted by a thought. When you are, just let the thought go and refocus on your breathing. Use this same process the next time you are in a conversation and a judgment arises
Listening
- Consider: How do you know when you are really listening to someone else? What behaviors and thoughts emerge?
- Begin to notice when you listen openly and when you don’t. Notice what situations block your ability to listen.
- Notice your internal responses when you are listening to someone else. What emotions and reactions arise when you sense resistance within yourself to listening? What arises when you do not resist?
- During a meeting or conversation, ask the following questions to listen for collective meaning: “What reality would make sense of all these diverse points of view?” or “If there were one voice speaking here, what would it be saying?”
Reflection
- Notice the nature of your relationship with silence. When are you comfortable with silence? Uncomfortable?
- Try pausing and taking a few breaths before answering a question. Notice any changes in the way you respond
- At the end of a meeting or one-on-one conversation, set aside a few minutes to reflect on the gathering’s major learnings, both in terms of the content talked about and the form of conversation you used.
Assumption Identification
- When you encounter a person with an opinion that differs from yours, ask yourself: “What filter am I looking through that is different from the one this person is using? What assumptions might underlie both our perspectives?”
- Notice how the assumptions you hold about different people influence the conversations that you have with them. Experiment with purposefully holding a different assumption about someone – and observe what happens.
- Use the Ladder of Inference to explore your own thinking and to inquire into the thinking of someone else who sees things differently than you.
Inquiry
- Next time you hear a comment that you don’t understand or that you think is wrong, try asking a question that will reveal more of the person’s thinking.
- Ask questions about the connections and possible relationships between diverse perspectives.
- Reflect on what it feels like to be curious. What behaviors and attitudes emerge from you when you are curious? Practice being curious, particularly in the face of disagreement.
Building a Safe Container. Another strategy for incorporating dialogue into your organization is what we call container building, or creating an environment to support dialogic forms of conversation. Container building entails arranging a safe place where all can speak their minds, where people explore questions like: “Why are we all here? Do certain things need to be said before each of us can be fully present for the conversation? What guidelines do we want to agree on that will support our purpose?” The goal of container building is to create shared meaning and intention about where you are as a group, where you’re going, and what practices will help you get there.
If a key purpose of dialogue is to promote learning, along with whatever other goal is at hand, we need to create an environment that supports authentic speaking and new ideas, an environment where the words dumb and mistake do not have a home. If a team member cannot say what he’s thinking, or if he’s withholding information that may be important to the team, how can learning take place and good decisions be made? All teams need an environment where everyone can get their cards on the table, so the team can play with a full deck.
Team leaders can play a central role in container building, through a dialogue principle that we call “suspension of status and roles.” No matter what level you occupy in your organization, it can be very hard to speak honestly in a meeting when your boss is in the room. In dialogue, we agree to do our best to temporarily suspend status and roles. Of course, these don’t disappear, but by suspending them, we become more conscious of power differentials and their impact on our communication. If you happen to be the leader in such a conversation, you can suspend your status – and contribute to container building – by actively practicing suspending judgment, listening, speaking later rather than earlier, and acknowledging and building on others’ comments.
Sustaining Energy and “Aliveness.” When learning occurs during a meeting or conversation, a feeling of energy and spark arises within the group. By intentionally asking questions like those that follow, everyone takes responsibility for keeping the conversation alive and valuable. “What is of interest to the group? Is what I’m saying adding to the conversation in a way that expands and/or deepens the picture? What are we learning?”
Stalking Dialogue Opportunities
If we assume that learning is happening all the time, then we can practice engaging in it day to day, rather than relegating it to certain times or locations, such as training rooms. By stalking dialogue opportunities, we can simultaneously promote learning. Where can we find such opportunities? Look for occasions in which people are grappling with decision-making, problem-solving, conflict work, visioning, and other challenges that strongly affect the whole group or organization. Below are some tips for using dialogue during these times
Problem-Solving and Decision Making. With both problem-solving and decision-making, groups focus on taking action. And though dialogue is not about immediate action, it is about building shared understanding of a problem in order to decide on the most appropriate action for the entire system. A good maxim here is “Dialogue first, decide second.” Establishing an environment for listening, inquiry, and reflection will take you a long way toward surfacing root causes to problems, reaching shared understanding of a problem, and avoiding decisions and solutions that may create short-term success but prove extremely costly in the long run (see “Opportunities for Dialogue”).
OPPORTUNITIES FOR DIALOGUE
Problem-Solving
- When faced with a stubborn, recurring problem, consider inquiring into people’s observations, the interpretations and assumptions they hold about the problem, and its possible solutions. Ask yourself, “Have we built shared understanding of the problem and its root causes before moving forward?”
- When you aren’t getting the results you desire, take a look at your assumptions and the thinking that led you to the decisions and actions that produced the result.
- Consider using periodic “What’s on your mind?” conversations within your group to create a forum in which emergent problems can be recognized and dealt with before they become full-blown crises.
Decision-Making
- When you are faced with an important decision that affects many people, consider holding a dialogue to ensure that all voices have been heard and that the thinking underlying the different alternatives has been surfaced before moving to a decision.
Conflict. Conflict also offers an excellent opportunity to practice dialogue. In fact, by using dialogue, you can turn conflict into a learning experience. We have seen this happen numerous times within work groups. One common source of conflict stems from differences in personal styles; for instance, some people want to move ahead quickly while others prefer a slower pace with time to reflect. When differences lead to conflict, we remind group members that dialogue is about suspending judgment of others’ behaviors and perspectives and about listening to understand. Second, we ask that people resist the urge to create guidelines or ground rules that inevitably validate one behavior or style and negate the other. The group will usually find a way of conversing that works for all involved .
Someone once said that “the opposite of one great truth is another great truth.” Acting on this, the next time you become embroiled in a conflict of opinion in your work team, try switching positions back and forth with your “opponent.” That is, argue for your side, then try arguing from the other side as your adversary now argues from your side. Ask yourselves, “What might we learn if we consider both sides to be right answers in a larger picture? And what larger picture might include both viewpoints?”
Visioning and Strategic Planning. For individuals, groups, or organizations to develop a meaningful strategy, they must first engage in some authentic conversation about purpose, values, and beliefs about how the world operates and how they want to be in relationship with that world. All too often, people crank out visions and strategies without ever stopping to examine the ground on which they stand, the assumptions they hold about how things work, and the implications of those assumptions for future dreams and plans.
Inquire into your assumptions about what is working in your company’s current reality and why; where you want to go and why; and how you think you might get there. Look for any inconsistencies or incompatibilities in assumptions that might lead to strategies and actions that are not coherent with your desired results. For example, you want to move toward a collaborative culture because you assume that by collaborating, people can craft creative solutions to daily challenges. On the other hand, you propose a reward strategy that compensates people for individual accomplishments because you assume that individuals will feel devalued if you don’t recognize them independently. These assumptions may both be valid, and yet if you don’t recognize how they may undermine one another, you will almost certainly send competing and confusing messages.
A lot of people talk these days about the need to “think out of the box.” It’s a great concept, but it’s very hard to do unless you first have a clear vision of the box. Dialogue can help by surfacing the assumptions that create your current reality. Then you can ask the question, “How would our assumptions and thinking need to change in order to create a different reality?”
Successes and Challenges
Where has dialogue been most successful, and, conversely, where has it faced the biggest challenges in organizations? Dialogue seems to have the most chance of success when it’s used by people who already have an affinity for and support its values. Such people might not yet be consciously aware of the skills and capacities involved, but they have an innate attraction for dialogue’s underlying principles.
Commitment from team leaders and members also increases dialogue’s chances of success. By leaders’ commitment, we mean managers’ support of people in their practice of dialogic communication skills, as well as their willingness to see and make changes in their own style. This approach means participating in the dialogue process, not simply supporting it from afar. And, when leaders are truly committed to the dialogic process, they do not mandate it. They recognize that to do so would be incongruent or inconsistent with the very values of dialogue. Instead, they invite employees to participate voluntarily.
Change agents or people who do organizational development work can be especially successful at bringing dialogue directly into how they are promoting organizational change. They may not call it dialogue, but it is clear that their facilitation style is dialogic in nature. These individuals pay attention to the way that people are taking part in conversations. Whether it’s a team-building session, visioning, or problem-solving or coaching session, they bring dialogic skills into those contexts and demonstrate the value of attending to conversational forms. They also encourage shared responsibility for the quality of conversation. By doing so, they shift responsibility for monitoring behaviors and setting ground rules from themselves to the group members We’ve also noticed that dialogue is successful when people talk about things that are really important to them. They are usually strategic in their use of the process and do not use dialogue as a blanket approach to any issue. They make choices about where dialogue skills are most appropriate and bring the highest value. By applying dialogue in this way, practitioners reinforce its value.
Still, as with every important tool, there are some challenges that come with incorporating dialogue in an organization. For one thing, we don’t recommend introducing dialogue in an atmosphere where there is little to support its use. When people are trained in dialogue but not supported in the ongoing, daily practice of it, their expectations will ultimately be dashed.
Another big challenge is that while dialogue often produces an immediate impact, the cultural changes that it supports don’t happen overnight. They may take years, perhaps even lifetimes. We have to recognize that dialogue can shift a culture dramatically, but it will do so over time. And that can be a challenge in a culture that wants quick fixes and immediate gratification.
We feel confident that dialogue will play an increasingly important role in the future in organizations. As dialogue works its way further into our consciousness, there will be more brave souls eager to learn it. The idea is to recognize and seize the opportunities for dialogue that make sense within your organization or community. By nurturing dialogue, both as it spontaneously emerges and in planned sessions, you’ll be well on your way to leading long-term organizational learning and change.
NEXT STEPS
- Convene a “What’s on your mind” forum. Invite people to talk about questions and issues that are important to them. Before beginning the conversation, ask participants to recommend four or five ground rules for creating a conversation where everyone can be heard. Then ask that each person choose one rule to focus on during the conversation. Another option is to pass around a “talking stick” to focus people’s listening and help create a slower pace.
- Organize an ongoing ”diversity group.” Invite people to talk about questions of diversity in the workplace to create greater shared understanding among the various groups in the organization. Plan to meet regularly. Because diversity issues can be volatile and laden with emotion, you may want to have a skilled facilitator participate in the beginning to help the group create a safe environment.
- Develop a new product using dialogue. See if you can identify your assumptions about what customers want/don’t want and what you think you can/cannot create. These are the “boxes” that will define how innovative you allow yourselves to be. Then ask questions like, “How would we need to change our thinking to imagine a completely different and innovative solution for this customer?”
Glenna Gerard and Linda Ellinor are co-founders of The Dialogue Group and co-authors of Dialogue: Rediscover the Transforming Power of Conversation (John Wiley & Sons, 1998). Glenna (ggunlimited@earthlink.net) has a consulting practice based in Laguna Beach, CA. She helps groups and organizations design environments and processes for powerful conversations. Linda (lellinor@home.com) is an organization consultant living in Dana Point, CA.

